The Alphavaccine Platform System
The Alphavaccine Platform System constitutes a major advance in vaccine technology and presents an opportunity to immunize against as well as treat new diseases as well as significantly improve existing vaccines.
Our system is genetically derived from a modified alphavirus. Using molecular biology and genetics, the virus is re-engineered, substituting a gene from an infectious disease or cancerous cell for a portion of the original viral genome. The re-engineered alphavaccine particles express the substituted gene (or genes), rather than producing more virus particles, thereby transforming the original virus into a highly effective vaccine system. For a more detailed explanation of how alphavaccine particles are produced, view the Alphavaccine Tour.
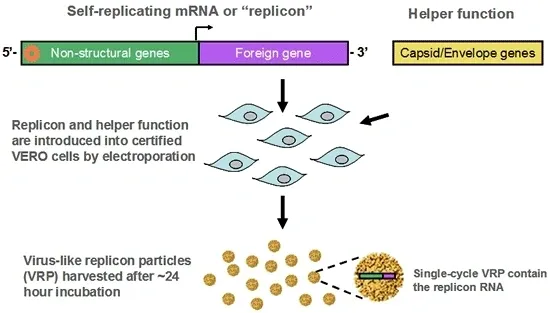
What Are the Advantages of Using alphavaccines?
The alphavaccine system has distinct advantages as a platform technology for vaccines. It is an ideal core technology because it:
The alphavaccine system is the only vaccine vector system that has the potential to deliver all of these highly desirable vaccine technology attributes.
Alphavaccines have shown excellent protection in numerous models for infectious disease and cancer, including influenza, CMV, breast cancer, melanoma, prostate cancer, SARS, HPV, HSV, RSV, PIV, Marburg and Ebola viruses, viral encephalitis viruses, and botulinum toxin. Protection has been demonstrated in over half a dozen species, ranging from mice to non-human primates.
